Para maximizar o potencial econômico e ambiental dos modelos de negócios circulares, as empresas precisam projetar produtos que sejam fisicamente duráveis, emocionalmente duráveis e que possam ser refeitos e reciclados ao final de seu uso.
Durabilidade física - Combinação de escolhas de materiais e construção de vestuário, incluindo reforço de componentes, para criar produtos altamente duráveis que possam resistir a danos e ser usados por longos períodos de tempo.
Durabilidade emocional - Aplicação de estratégias que aumentam e mantêm a relevância e a conveniência de um produto para um usuário, ou vários usuários, ao longo do tempo.
Remanufatura e reciclabilidade - Projetar produtos para que possam ser desmontados e seus componentes e materiais possam ser refeitos ou reciclados em novos produtos.
Todas as três considerações de design são cruciais para o desenvolvimento de produtos para modelos de negócios circulares. No entanto, provavelmente haverá algumas compensações para essas considerações de projeto devido a fatores como as tecnologias atuais e as soluções de materiais. É essencial que as decisões de projeto sejam especificamente adaptadas para maximizar os resultados econômicos e ambientais de cada modelo de negócio individual.
Projeto para durabilidade física
A durabilidade física é um fator fundamental para o sucesso de muitos modelos de negócios circulares. Por exemplo, um modelo de aluguel com alta rotatividade não será eficaz, a menos que os itens alugados tenham sido projetados para resistir a limpezas frequentes. Para criar produtos altamente duráveis que possam resistir a danos e desgaste por longos períodos de tempo, é necessário que os designers combinem cuidadosamente as opções de materiais e a construção do vestuário, incluindo o reforço dos componentes.
Exemplos de empresas que colocam isso em prática
W. L. A Gore and Associates avalia o desempenho de seus produtos na vida real e coleta comentários, além de realizar testes de laboratório que imitam o envelhecimento em uso real. A empresa usa isso para informar o design dos produtos, como, por exemplo, aumentar a durabilidade dos componentes que falham primeiro.
A Lacoste está aplicando padrões de durabilidade em todas as categorias de produtos têxteis. Para isso, a empresa introduziu um
como parte de sua estratégia "Elegância Durável". Ele também leva em conta os hábitos e as preocupações dos clientes, abrangendo tanto os componentes individuais quanto os testes de produtos acabados.
A ERDOS se concentra no desenvolvimento de produtos de caxemira de alta qualidade. Sua coleção SHAN 2019 incluiu caxemira "autolimpante", que é resistente à água e ao óleo e de fácil manutenção. A empresa usa uma técnica de tecelagem que não precisa de costura, economizando materiais e energia e tornando o produto mais durável. Devido à alta durabilidade física de seus produtos, a ERDOS é capaz de oferecer serviços de reparo e manutenção (ou seja, seu "serviço de atendimento pós-venda").
Projetando para durabilidade emocional
As roupas também precisam manter sua relevância e conveniência para os clientes ao longo do tempo. A durabilidade emocional, relacionada ao tempo que as pessoas desejam usar um produto, é necessária. A durabilidade física por si só não é suficiente. A durabilidade emocional pode se basear em fatores como atemporalidade, raridade, história e significado, entre outros aspectos.
Uma oportunidade de estender a durabilidade emocional de um item pode ser o compartilhamento de histórias sobre como o produto foi feito para ajudar a criar apego. Da mesma forma, oferecer serviços de personalização para tornar os produtos exclusivos para um usuário pode aumentar o desejo dos usuários de usar esse produto nos próximos anos.
Exemplos de empresas que colocam isso em prática
A Beyond Retro
se concentra em desenvolver e enfatizar a exclusividade de seus produtos (por exemplo, produtos refeitos a partir de itens usados selecionados). A marca criou uma equipe dedicada, responsável pelo desenvolvimento de exibições teatrais em lojas de varejo e pela curadoria de produtos exclusivos.
A klee klee
compartilha histórias sobre cada um de seus produtos para que os clientes possam saber de onde vêm os materiais, como a peça foi feita e como cuidar dela, ajudando, assim, a criar um vínculo mais forte entre o cliente e a roupa.
A ARKET seleciona materiais que melhoram sua aparência e sensação com o aumento do uso e fornece guias de cuidados para esses materiais, como jeans.
Projetar roupas para serem refeitas ou recicladas
Para que os modelos de negócios circulares sejam bem-sucedidos na redução das emissões de gases de efeito estufa a longo prazo, as novas roupas precisarão ser fabricadas com materiais que já estão em uso e deixar de usar recursos virgens finitos. Para que isso seja possível, os produtos precisam ser projetados e fabricados de forma que possam ser desmontados, refeitos e reciclados, o que significa considerar como os produtos são construídos, bem como quais materiais e componentes são usados. Isso também evita que os produtos se tornem resíduos e pode maximizar ainda mais os resultados ambientais positivos.
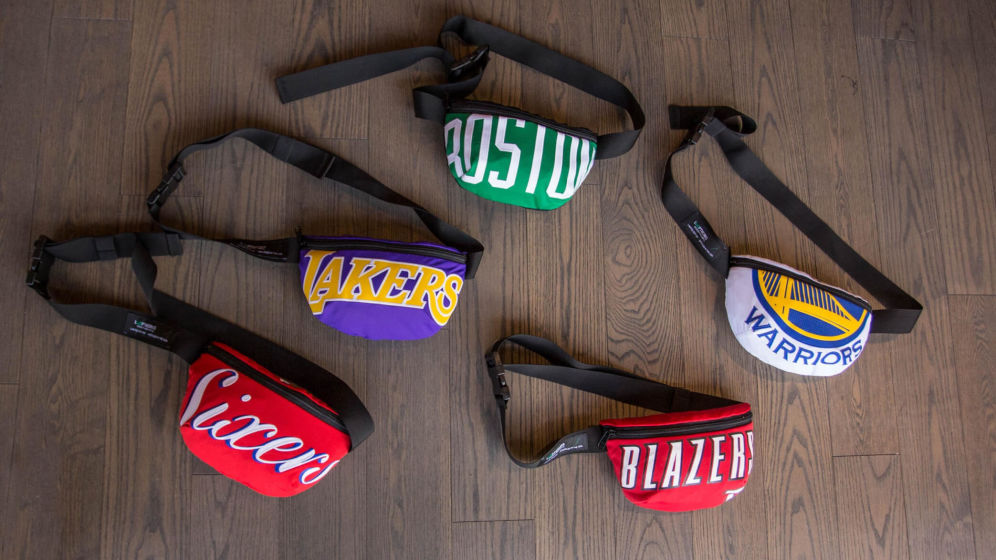

A Looptworks colabora com empresas para reaproveitar materiais, como essas bolsas feitas com camisetas usadas da NBA.
Exemplos de empresas que colocam isso em prática
A For Days fabrica suas roupas com tecido 100% celulósico (predominantemente algodão orgânico) para que possam ser facilmente transformadas em novas peças ou recicladas quando estiverem gastas. A For Days incentiva seus clientes a devolverem suas roupas usadas para que possam refazê-las e reciclá-las na prática.
Para sua série Circular de jaquetas, a Napapijri simplificou o design de modo que toda a jaqueta - tecido, enchimento e acabamentos - seja fabricada com um polímero reciclável - Nylon 6. Os clientes podem devolver os produtos da linha Circular Series após o uso, para que possam ser refeitos e reciclados em novos produtos.
A Looptworks está colaborando com outras empresas para reutilizar materiais pré e pós-consumo. Por exemplo, a empresa fez uma parceria com a NBA para transformar camisas usadas em mochilas e bolsas crossbody. Essas parcerias ajudam as empresas a evitar o desperdício e, ao mesmo tempo, proporcionam a elas uma melhor compreensão de como reprojetar seus produtos.
O que os formuladores de políticas podem fazer para estimular o design de produtos que garantam que os itens sejam usados mais e por mais tempo
As políticas de produtos existentes geralmente têm se concentrado no desenvolvimento de referências inspiradoras e critérios de design em rótulos ecológicos voluntários ou em compras públicas ecológicas. Essas políticas podem ser desenvolvidas com foco na durabilidade física e emocional, além de refazer e reciclar. Com base em uma avaliação completa do impacto ambiental, os formuladores de políticas podem estabelecer requisitos regulatórios mínimos referentes a informações obrigatórias e padrões técnicos para garantir que os produtos sejam feitos para durar e nunca se tornem lixo.
Baixar
Os modelos de negócios circulares estão disponíveis em: inglês
Quatro ações fundamentais para as empresas
Para garantir que seus modelos de negócios sejam circulares e para maximizar os resultados positivos, as empresas, com o apoio dos formuladores de políticas, podem adotar quatro ações principais.