This page is part of the report Building Prosperity: Unlocking the Potential of a Nature-Positive, Circular Economy for Europe. Explore the full report to delve into all focus areas, strategies, and key recommendations, or browse the entire case study collection to see these strategies in action.
Strategy: Revitalising brownfield land
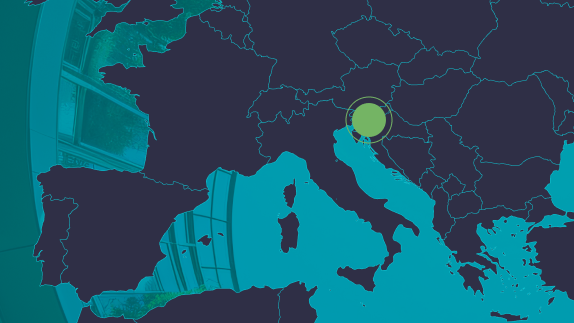
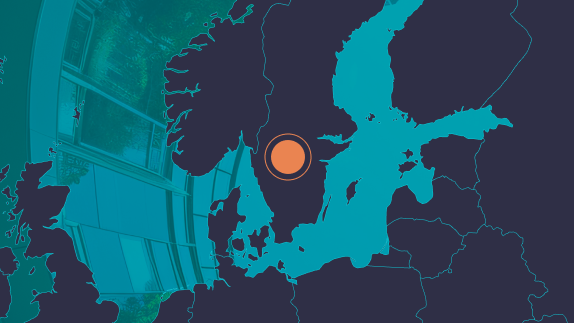
Location: Hamburg, Germany
Organisation: HafenCity
In Hamburg, the transformation of a former industrial port area stands as a pioneering model of circular and nature-positive urban development. Spanning 157 hectares, HafenCity, the new downtown area on the waterfront, has increased Hamburg’s city area by 40% while avoiding green field expansion. The mixed-use, high-density development maximises the adaptive reusereuseThe repeated use of a product or component for its intended purpose without significant modification. of existing buildings and infrastructure. HafenCity is projected to accommodate 15,000 residents in approximately 8,000 homes, with about 25% being subsidised to promote social diversity. Additionally, the project comprises a university campus for 7,000 students and the creation of up to 45,000 jobs is anticipated.
As Europe’s largest inner-city urban development project, HafenCity is a test-bed for innovative, climate-friendly building solutions. A key feature of HafenCity is the commitment to public green spaces, with 25% of the area dedicated to squares, parks, and promenades, enhancing biodiversity, liveability, and reducing flood risks. Utilising the city’s district heating system, the buildings are designed with high energy efficiency standards, and are all connected to a district heating system. The street layout prioritises smart mobility solutions mainly walking, cycling, and public transport, reducing the need for private car ownership.
At the heart of HafenCity’s development strategy is an innovative public-private partnership model: HafenCity Hamburg GmbH. This model ensures high standards in urban design while facilitating swift and efficient project execution, avoiding the common pitfalls of public sector delays. Investment for the project was via EUR 10 billion of private funds and EUR 3 billion in public investment, the latter mostly financed through strategic land sales.
HafenCity exemplifies how visionary planning combined with robust cross-sector collaboration can transform dilapidated industrial areas into thriving, low-carbon communities integrated with nature. It provides a replicable model for inclusive, circular urban renewal.